Breadcrumb
Numerical investigation of hematocrit variation effect on blood flow in an arterial segment with variable stenosis degree
Numerical simulations of blood flow in arteries are important in the understanding and diagnosis of many cardiovascular diseases, such as atherosclerosis and arterial stenosis. More realistic mathematical models representing blood rheology offer a better understanding of these diseases. In this study, blood is considered an Oldroyd-B fluid with a shear-thinning property and a shear rate-dependent relaxation time that is adopted by fitting experimental data. The Quemada model is used to represent the shear-thinning property with hematocrit variation. The stabilized finite element method is used
Centralized Multi-agent Mobile Robots SLAM and Navigation for COVID-19 Field Hospitals
In this paper we focus on the proof of concept prototype of fully autonomous centralized Multi-Robot System (MRS) consisting of a Hexapod walking robot and a six wheeled mobile robot. Recently, there has been an increasing demand for such systems as they can be involved in several tasks such as collaborative search and rescue, surveillance, monitoring, and disinfecting Field hospitals. To name a few, COVID-19 pandemic showed the weak points in the medical sector around the world, including those in the most advanced nations that had to go through hard decisions due to the lack of medical
Ergonomic analysis of a working posture in steel industry in Egypt using digital human modeling
This study presents solutions for improving a bending awkward posture in steel industry in Egypt using digital Human Modeling (DHM). The information is gathered by interviewing the workers, working postures are recorded via a video camera while the worker is performing his usual work. The postures are analyzed using DHM software. Porter comfort analysis and Rapid Upper Limb Assessment are applied for postures analysis. The analysis shows high levels of discomfort in neck, trunk, leg and forearm. These discomforts could cause permanent injuries over long periods. A modified design is proposed
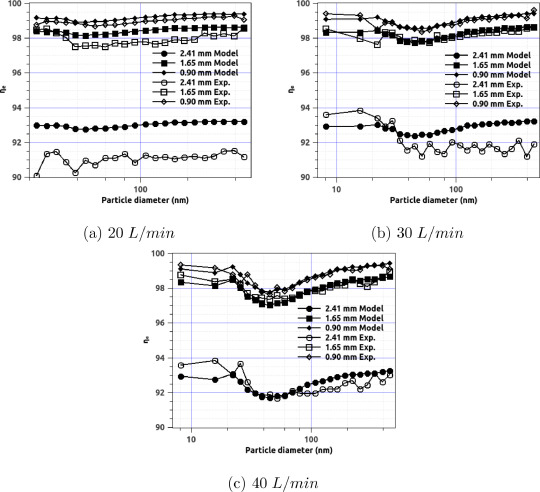
An analytical model for the effective filtration efficiency of single and multiple face masks considering leakage
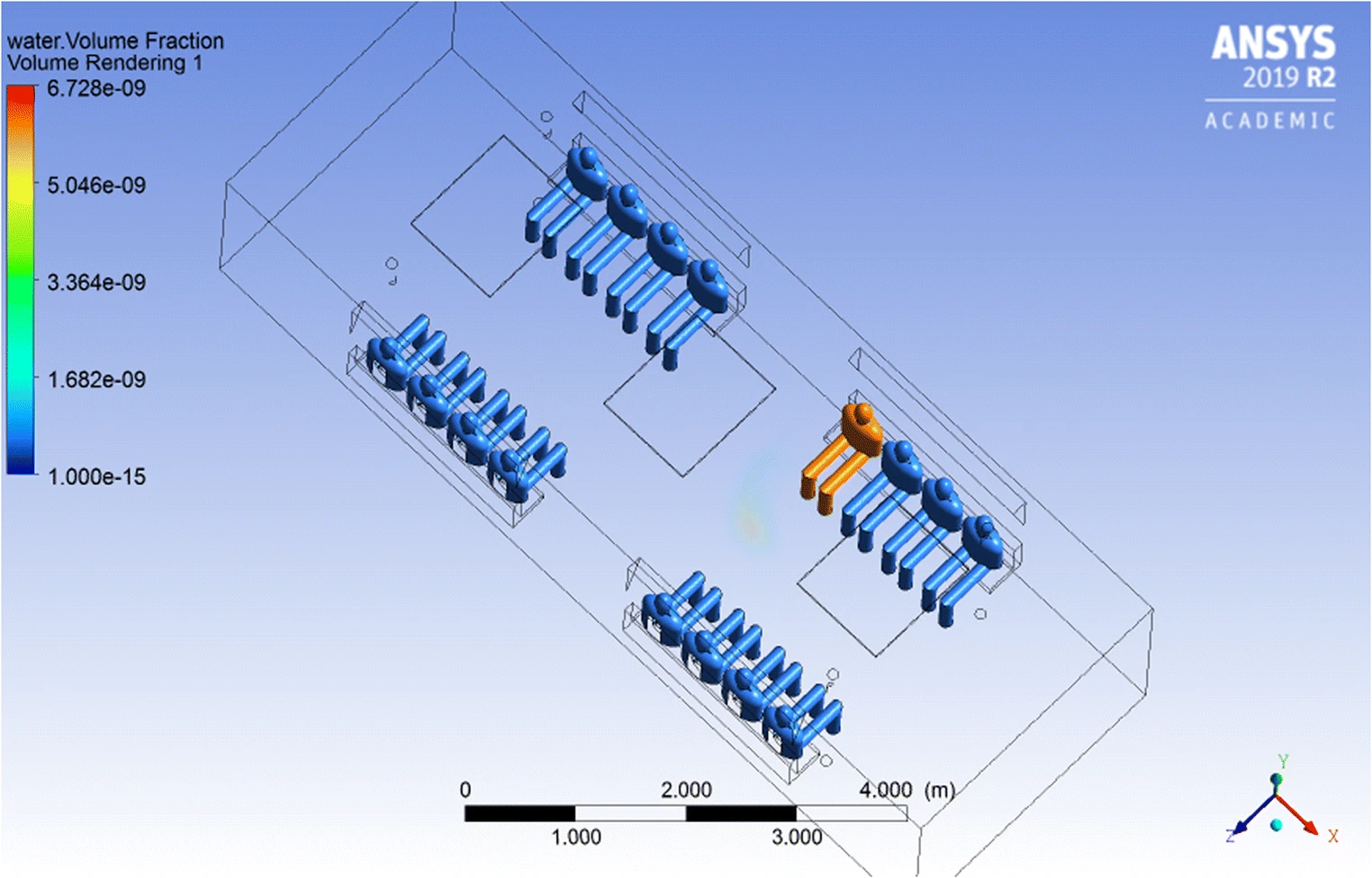
Air change rate effects on the airborne diseases spreading in Underground Metro wagons

Design of a Schlieren System for Visualization of Heat and Mass Transfer
In this contribution, a simple yet effective design for Schlieren photography system is described and implemented. The proposed system is used in the visualization of both heat and mass transfer phenomena. Refractive index gradient is created by a lighter to study mass transfer, then the lighter is ignited to create temperature gradient. Results show the ability of the proposed system in capturing the gradients in both mass and temperature gradients. © 2020 IEEE.
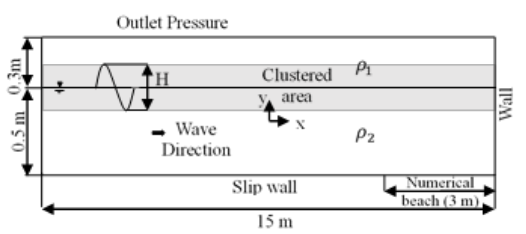
Simulation of Water Wave Interaction with Large Submerged Square Obstacles
Modified P3HT:PCBM Active Material with LiF Vertical Cylinders for Organic Solar Cells
In this paper, we introduce active material for an organic solar cell with a modified composition. A combination of P3HT: PCBM with parallel vertical LiF cylinders formulate the active material structure. The collection efficiency in the active material reaches 92.2%. The operating wavelength where the maximum collection efficiency occurs is adjusted and matched with the wavelength where the maximum irradiance of the solar spectrum occurs. The absorption per unit volume of the new structure is 80.4 μm-3 while the blank structure is 75.07 μm-3. The net absorption magnitude for the required
Analytic and numeric analysis for deformation of non-prismatic beams resting on elastic foundations
Background: The buckling load as well as the natural frequency under axial load for non-prismatic beam is a changeling problem. Determination of buckling load, natural frequency, and elastic deflection is very important in civil applications. The current paper used both perturbation method (PM), analytic method, and differential quadrature method (DQM), numerical method, to find buckling load and natural frequency with different end supports. The deflection of the beam resting on an elastic foundation under transverse distributed and axial loads is also obtained. Both PM and DQM are used for
Analytical solution for nonlinear interaction of euler beam resting on a tensionless soil
The nonlinear interaction between an elastic Euler beam and a tensionless soil foundation is studied. Exact analytical solutions of the challenging problem are rather complicated. The basic obstacle is imposing compatibility conditions at lift-off points. These points are determined as a part of the solution although being needed to get the solution itself. In the current work, solutions are derived using the approximate Rayleigh-Ritz method. The principal of vanishing variation of potential energy is adopted. The solution is approximated using a set of suitable trial functions. Lift-off
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 19
- Next page ››

