Breadcrumb
Underwater Soft Robotics: A Review of Bioinspiration in Design, Actuation, Modeling, and Control
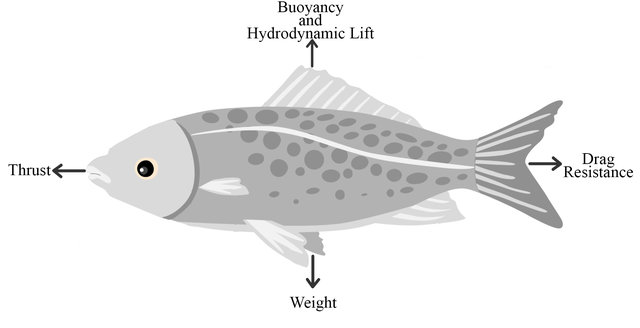
Nature and biological creatures are some of the main sources of inspiration for humans. Engineers have aspired to emulate these natural systems. As rigid systems become increasingly limited in their capabilities to perform complex tasks and adapt to their environment like living creatures, the need for soft systems has become more prominent due to the similar complex, compliant, and flexible characteristics they share with intelligent natural systems. This review provides an overview of the recent developments in the soft robotics field, with a focus on the underwater application frontier. ©
Systematic university decision making based on footprint identifiers
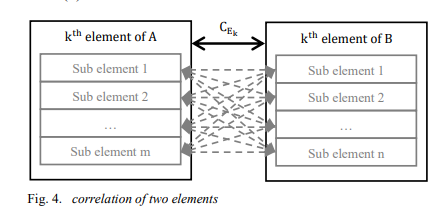
A new systematic decision-making framework for universities is presented. The framework avoids the disadvantages of the balanced score cards technique. A solid mathematical technique is provided for mapping processes and quality items. Application to the Egyptian system is fully explained. The footprint concept developed within an international initiative is introduced. The mathematical correlation algorithm main output is a decision matrix matching processes and quality aspects. Results illustrate automatic suitable matching between processes and quality standards. © 2021 IEEE.

Regression Modeling for the Ventilation Effect on COVID-19 Spreading in Metro Wagons
The effect of different ventilation parameters on the infection potential of COVID-19 in a metro wagon is numerically studied. Two key indicators are used to quantify this potential. Based on the numerical results a regression analysis is performed to come up with the most suitable regression model for these key parameters. The proposed regression models are helpful in quantifying the infection risk at different ventilation scenarios. © 2021 IEEE.
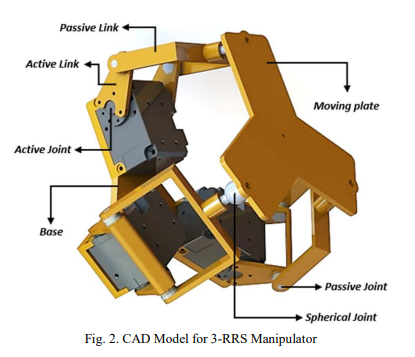
Design, simulation, and kinematics of 9-DOF Serial-Parallel Hybrid Manipulator Robot
Serial manipulator robot is one of the most advanced robots in the last decade. The demand for this type of robot leads the researchers to develop and improve the robot to increase its workspace, speed and to minimize the control complexity. This paper presents a novel robot configuration that combines a 6 DOF serial manipulator with a 3 DOF spherical parallel wrist. The serial manipulator is KUKA kr6 R900 type, which is a real industrial robot. At the same time, the parallel spherical wrist is 3-RRS type (Revolute- Revolute-Spherical Joint), which can support one translation movement in the Z
Solving Inverse Kinematics of a 7-DOF Manipulator Using Convolutional Neural Network
This paper presents a way to solve inverse kinematics of a 7-DOF manipulator using artificial neural networks. The manipulator consists of a 6-DOF articulated arm installed on a linear guide system to increase the workspace of the robot. The purpose of this paper is to provide an alternative to the traditional and complicated way to solve inverse kinematics by using artificial neural networks. The training data is generated from MATLAB after obtaining the DH parameters and workspace of the manipulator. Then, it was fed to the convolutional neural architecture to obtain a model for the
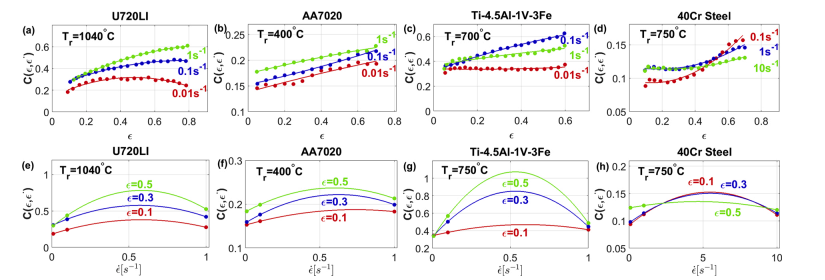
An improved generic Johnson-Cook model for the flow prediction of different categories of alloys at elevated temperatures and dynamic loading conditions
This paper presents a generic model for material flow prediction based on the well-known Johnson-Cook model. The model is developed to precisely predict the flow behavior of various categories of alloys. The coupled effects between strain, strain rate, and temperature were taken into consideration. The proposed model is developed and assessed using the hot deformation data of four different categories of alloys; with four different base elements. Besides, the data of two different alloys under dynamic loading are used for assessment. The proposed modification is compared to the original
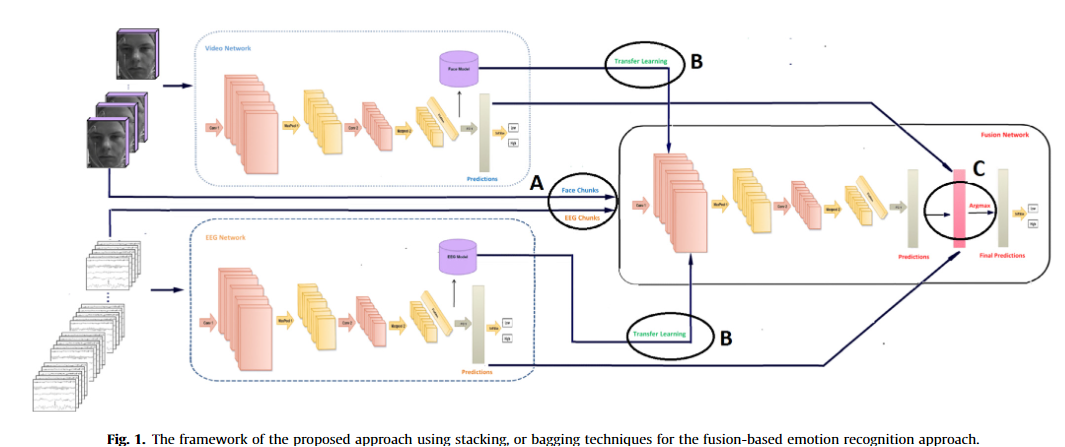
A 3D-convolutional neural network framework with ensemble learning techniques for multi-modal emotion recognition
Nowadays, human emotion recognition is a mandatory task for many human machine interaction fields. This paper proposes a novel multi-modal human emotion recognition framework. The proposed scheme utilizes first the 3D-Convolutional Neural Network (3D-CNN) deep learning architecture for extracting the spatio-temporal features from the electroencephalogram (EEG) signals, and the video data of human faces. Then, a combination of data augmentation, ensemble learning techniques is proposed to get the final fusion predictions. The fusion of the multi-modalities in the proposed scheme is carried out

An energy-utilization metric for heat transfer devices
A new metric for measuring the performance of heat transfer devices, which require the consumption of mechanical power to function, is proposed. The proposed Energy-Utilization Metric, EUM, is derived to quantify the achieved heat transfer rate per unit consumed mechanical power. By virtue of its definition, using the EUM as a preference metric between different heat transfer devices guarantees the selection of the design with the best energy-utilization characteristics or in other words the device which meets the required heat load with the minimum amount of consumed pumping power. The
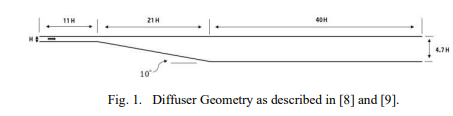
Comparative Study for Different URANS Models for Capturing Flow Separation Inside a Plane Diffuser
A comparative numerical study is performed among different URANS turbulence models investigating the ability of the models to capture the deformation of the boundary layer near the separation zone. The results are validated against previously published numerical works (URANS, LES, DNS) and experimental works. The comparison included grid resolution, the pressure distribution, and the velocity profiles at the inclined wall, then the streamlines plot of each model is used to properly estimate the separation and reattachment points. © 2021 IEEE.
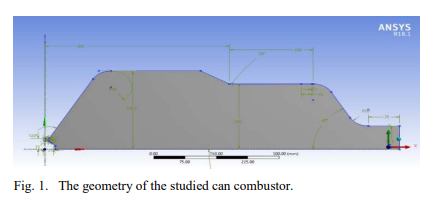
The Effect of Different Design and Operational Parameters on the Performance of Can-Type Combustors
Numerical simulation of the non-premixed combustion of methane air mixture in a gas turbine can- type swirl combustor is conducted. The study objective is to examine the effect of different design and operational parameters on the combustor performance and its emissions. The investigated parameters are the primary air flow rate, the swirl ratio between the secondary and the primary air and the fuel to the primary air swirl ratio. Several indicators are used to evaluate the combustion performance and emissions which include average exit temperature of the chamber, pattern factor, NOx and CO
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 2
- Next page ››
